Intelligent Sensing Technology
From analog sensing to digital sensing
nami innovates through:
- Motion, with wider coverage than other sensing (e.g., PIR sensors,) and filtering out vacuum bots and pets
- Occupancy sensing, detecting micromotion (e.g., breathing patterns)
- Fall detection with wider coverage than PIR or radar.

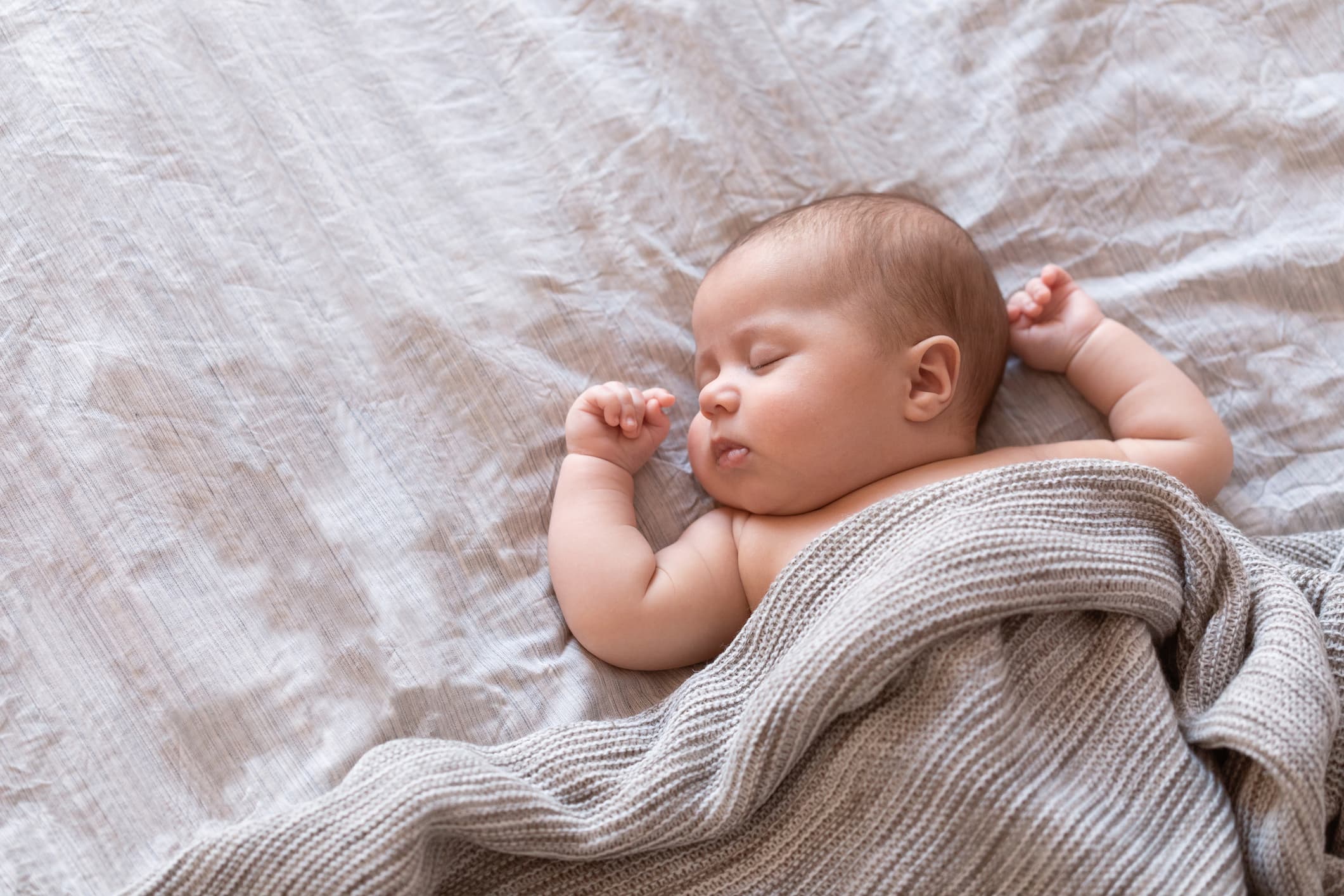
Digital sensing for monitoring wellbeing
Alongside wifi sensing, we provide acoustic sensing solutions to help protect vulnerable family members. Our technology can figure out if a baby is sleeping well, or interact with a person who has fallen to assess their needs.

Digital sensing for monitoring property
Intelligent sensing for smarter home and digital buildings doesn’t stop with human presence detection. Our digital platform means users can seamlessly deploy air quality sensors, acoustic listeners for smoke and CO alarms, and water flood sensors.

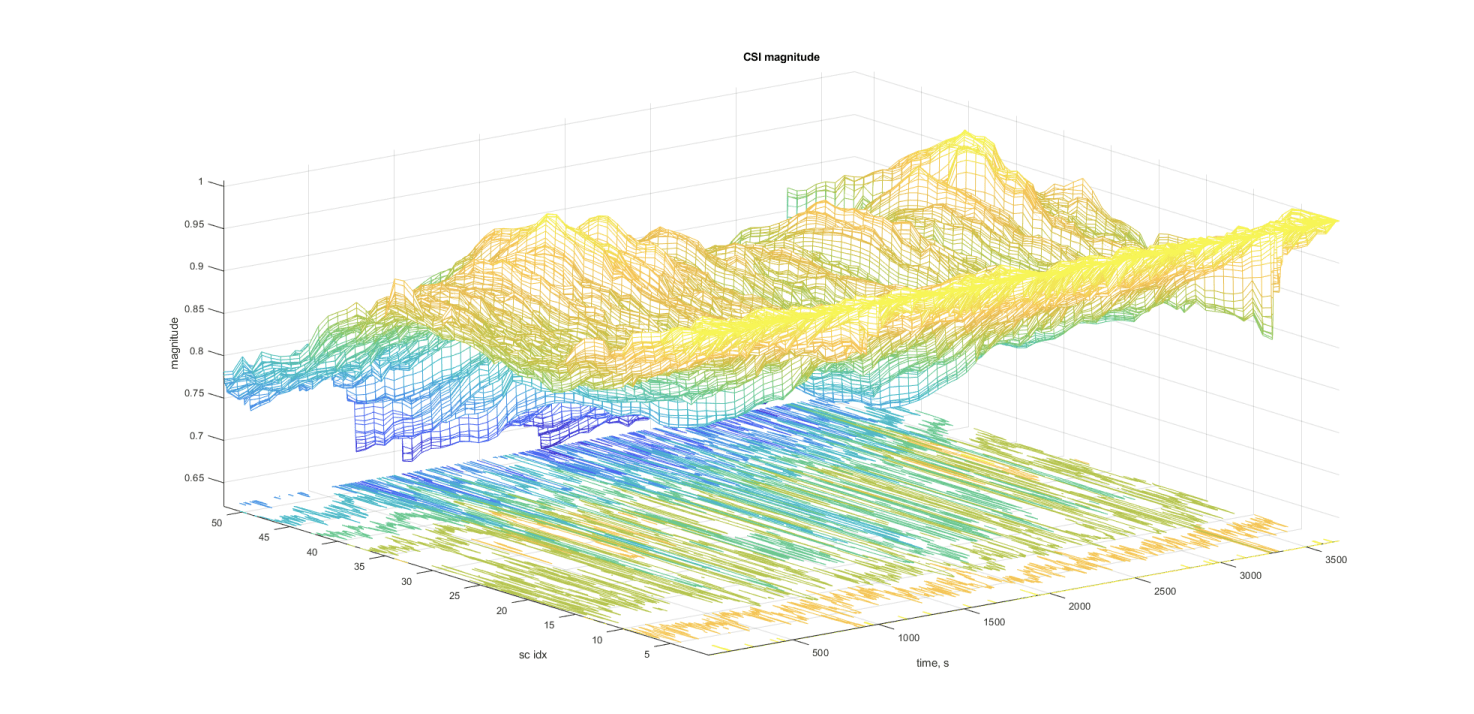
About Wi-Fi Sensing
Wi-Fi sensing is the detection of motion, presence and activity patterns through disruptions in Wi-Fi signals. Wi-Fi sensing technology measures the extent to which living objects distort the signals or waves emitted from transmitters to receivers.
nami modules collect, process and analyse Channel State Information (CSI) data 30+ times per second to sense activity in the environment.
Wi-Fi Intelligent Sensing
Easy to set up
It has wide coverage — it ‘sees’ through walls and objects with a minimum # of nodes.
It has deep granularity — it can distinguish humans from pets and other minor movements.
Is interoperable with most existing IoT applications.
Protects the privacy of occupants as no personal data is collected.
Enable recurring revenue opportunities for device makers.

Privacy at its core
nami technology is privacy by design, meaning nami does not collect the personal information of users. It achieves this through:
- No indoor cameras, as motion is detected through wifi sensing. There is no need to visually identify intruders
- No voice recording or storage, as acoustic sensors pick up certain sounds but do not record
- Superb data management practices, including rigorous encryption protocols, both at nami and with our partners, ensure that data is protected.
How does nami compare to other smart building tech?
For many years, homes and buildings have been fitted with technology that can sense motion. However, as you can see from the image below, they are no match for nami’s Wi-Fi sensing.
- PIR sensors use infra-red technology to recognize movement based on body temperature. While affordable, these sensors can be difficult to deploy, have limited coverage, fail to accurately distinguish humans and pets, and do not integrate well with other tech.
- Radar is a more costly option for smart buildings.
- Indoor cameras are a privacy risk due to their personal identification of individuals. They are also ‘line of sight’ only, and therefore vulnerable to blindspots.
| PIR Sensor | Radar | AI Indoor Camera | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment Ease | ||||
| Coverage | ||||
| Granularity | ||||
| Interoperability | ||||
| Privacy | ||||
| Cost | $ | $$ | $$$ | $$$$ |




nami vs PIR
Passive infrared (PIR) sensors continue to be a common component of motion detection systems. As with Wi-Fi sensing, it does protect the privacy of individuals. However, PIR has a range of disadvantages compared to Wi-Fi sensing:
- Coverage is poor as motion must occur in 'line of sight'. Wi-Fi sensing, by contrast, can 'see through walls'
- Information is not fine-grained, and false positives are common
- PIR is not easily interoperable with other tech.
nami vs radar sensing
Radar sensing interprets the 'echo' from radio waves interacting with solid objects. Like, Wi-Fi sensing, it is privacy-conscious and allows non-line-of-sight monitoring. However:
- It has a significantly higher rate of false positives than Wi-Fi sensing
- It has a smaller field of coverage, due to only picking up motion in front of a narrow 'beam'
- It is generally expensive and requires professional installation.

nami vs cameras
Cameras provide clear identification of any intruders, and are therefore a common part of motion detection systems. However, cameras have a range of disadvantages compared to Wi-Fi sensing including that
- Indoor video cameras constitute a privacy risk
- Video cameras are line-of-sight-only, so do not provide full coverage of an area with physical obstacles
- Video cameras are relatively expensive, and generally require professional installation.

