Our platform
What is Wi-Fi sensing?
Wi-Fi sensing is the detection of motion, presence and activity patterns through disruptions in Wi-Fi signals. Wi-Fi sensing technology measures the extent to which living objects distort the signals or waves emitted from transmitters to receivers.
Our nami modules collect, process and analyse Channel State Information (CSI) data 30 times (and more) per second to sense activity in the environment.

Small is agile
The foundation of our sensing network are small, cost-efficient, easy to source but powerful Wi-Fi modules. Each device has its own unique certificate to connect to the cloud. Data is encrypted at rest and in transit.

Antennas I mesh network
The cornerstone for Wi-Fi sensing is radio frequency performance. We’ve invested heavily in R&D to design antennas which fit neatly into our devices while maintaining the highest sensitivity. Our patent-pending mesh system ensures optimal resource usage and maximizes reliability.
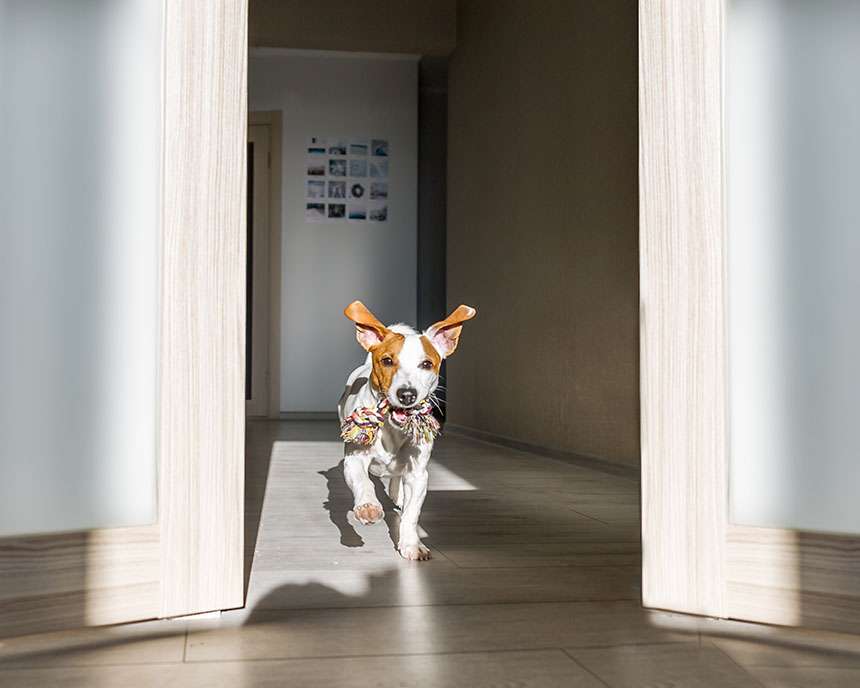


Motion detection
We achieve pinpoint accuracy in motion detection through either existing Wi-Fi devices, or performance-optimized nami hardware, able to distinguish humans from pets and other movement.
Our motion detection engine operates in a non-line-of-sight environment, ‘seeing’ through walls and achieving full-home coverage.
Presence sensing
Through a sophisticated, patented, process, nami devices store the radio frequency environment in a room when it’s empty. Our technology uses an optimized antenna array which analyzes real-time information based on micro-motion activity analysis (like breathing), to determine whether there’s anyone actually in the room.


Fall detection
We’re able to quickly and reliably detect potential life-threatening situations (like falls, heart attacks, an inability to get back up), with our on-device processing using dual-core MCUs able to sample the environment 1,500 times per second.
How does nami compare to other smart building tech?
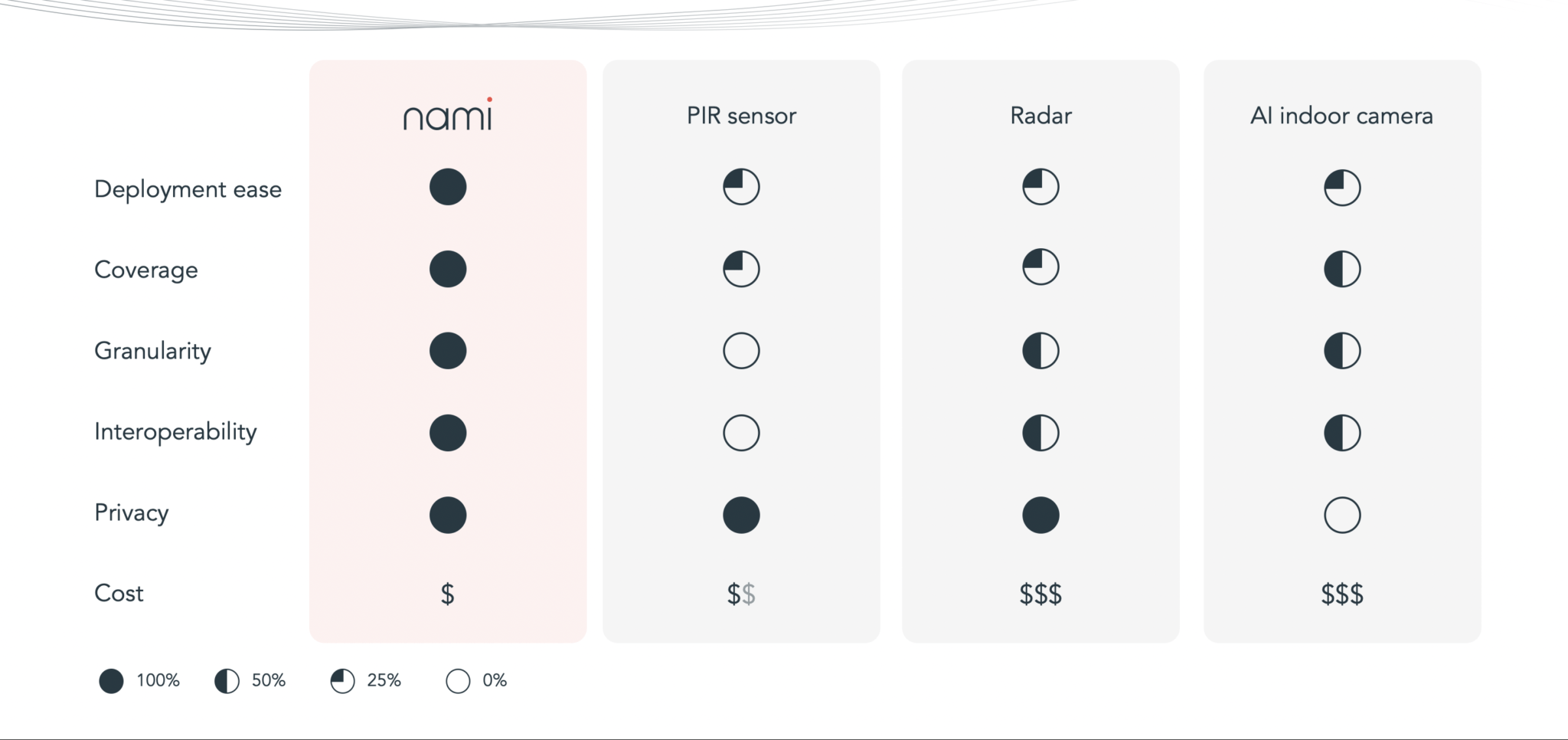
For many years, homes and buildings have been fitted with technology that can sense motion. However, as we demonstrate in the table below, they are no match for nami Wi-Fi sensing.
- PIR sensors use infra-red technology to recognize movement based on body temperature. While affordable, these sensors can be difficult to deploy, have limited coverage, and fail to accurately distinguish humans and pets.
- Radar is effective, but a more costly option for smart buildings
- Indoor cameras are a privacy risk due to their personal identification of individuals. They are also ‘line of sight’ only, and therefore vulnerable to blindspots.
Wi-Fi sensing, by contrast, means:
- Easy set-up — ready in 5 min
- Wide coverage — non-line-of-sight motion sensing ‘sees’ through walls and objects
- Deep granularity — it can distinguish humans from pets and other minor movements
- Interoperability with most existing IoT applications
- Protecting the privacy of occupants as no personal data is collected
- Affordability — nami technology is cost-effective and can be easily integrated with existing products
- Revenue-generating opportunities. Existing IoT, consumer electronics, ISP products and smart devices can benefit from Wi-Fi sensing ‘add-on’ features. It is an opportunity for additional, monthly, subscription-based revenue.